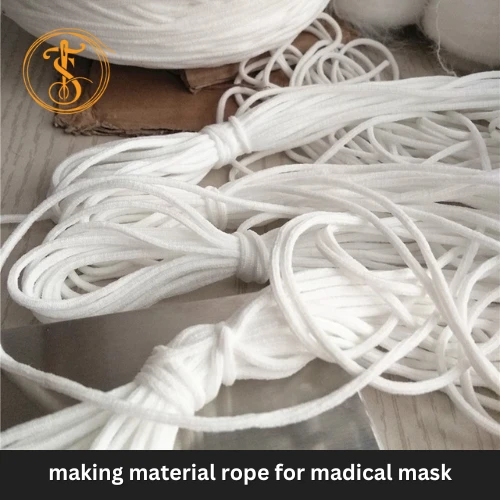
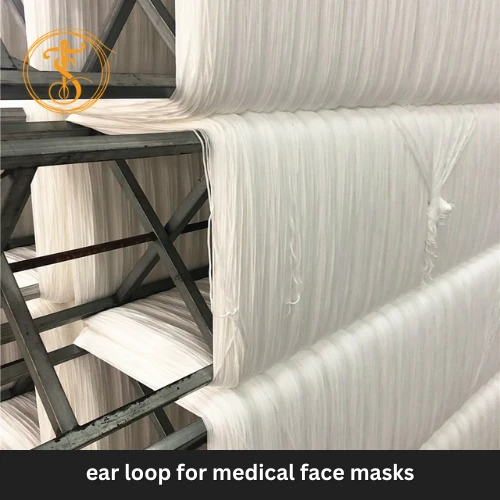
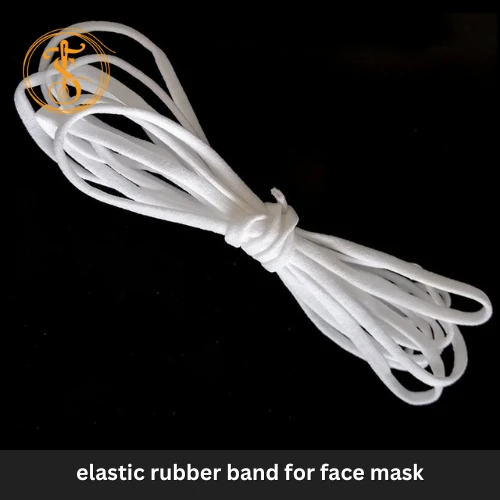
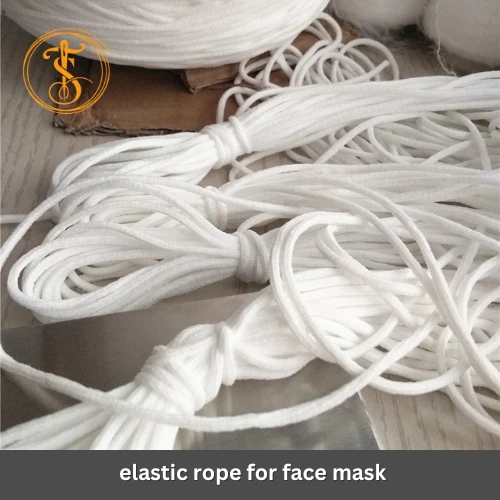
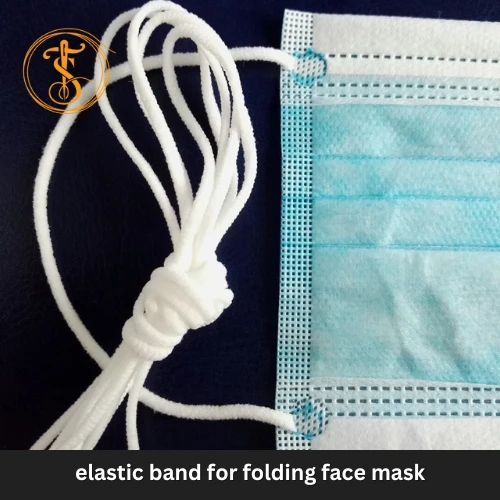
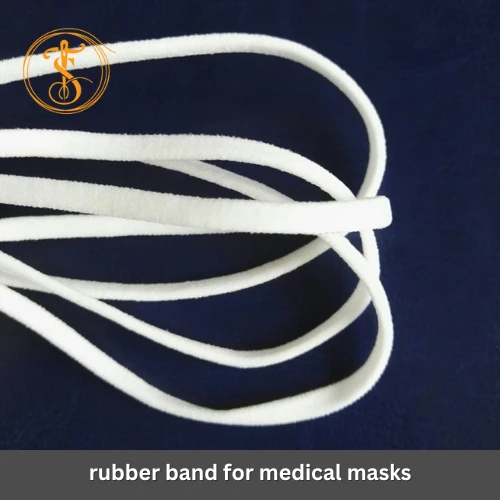
Yarn
All Yarn Products
(24 items)
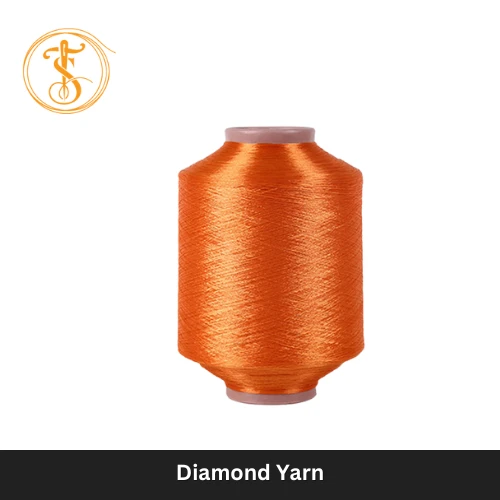
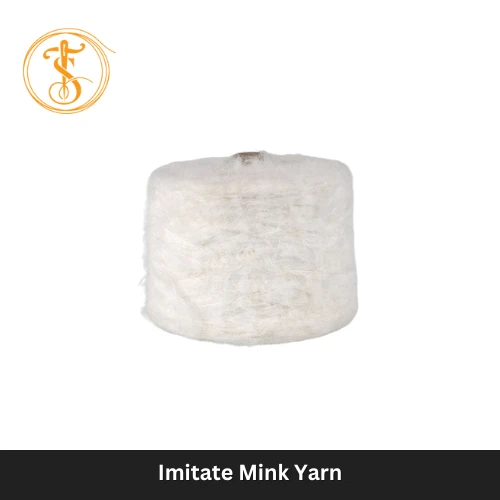
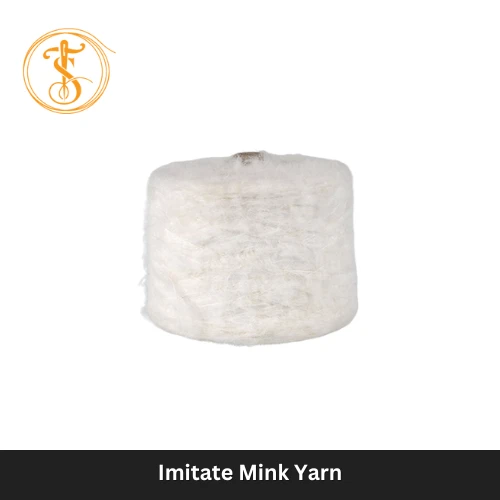
Yarn refers to the thread made of a twisted aggregation of fibers used for knitting and weaving. It is also a continuous staple and filament yarn strand combined as a suitable assembly. Yarn is well-made from natural materials, such as cotton, wool, and silk, on the other hand, the yarn also comes from synthetic or human-made materials, for instance, polyester, nylon, acrylic, as well as spandex. Types of Yarn: Several yarn types are there, starting from ring-spun yarn to cabled yarn. Let’s briefly describe each of them. The Two major Yarn Types are: 1. Ring Spun Yarn: These yarns are well-produced on the system of ring and traveler from different fiber types. 2. Flat Continuous Filament Yarn: These man-made yarn are produced in mono or multi-filament forms. Spun Yarn Types: 1. Rotor Spun Yarn: These yarns are well-consisted of fibers, twistedly bound together. Mostly, they are available in short staple fibers. 2. Friction Spun Yarn: These yarns are produced on the spinning system, using two rotating rollers in collecting fibers. Filament Yarn Types: 1. Textured and Continuous Filament Yarn: They are man-made continuous filament yarns, modified by a subsequent process to introduce loops, and coils into the filaments. Other Types of Yarns: 1. Twist Less Yarn: They come from staple fibers where the fibers are adhesively consolidated. 2. Core Yarn: There is a central core wrapped with staple fibers, produced in a single operation. 3. Self Twist Yarn: These yarns are two-ply yarns, produced in the operation where each component is well-twisted in alternating directions. 4. Piled Yarn: In a single operation, a yarn where two or more single yarns remain twisted together. Cabled Yarn: Cabled yarn is a yarn where two or more folded yarns remain twisted together. These yarns are produced from staple yarn. Application of Yarn Especially in the industry of textile, yarn is significant for most of the use. The application areas are: a) Sewing: Sewing is done by Hand or machine-based sewing machine. b) Knitting: Producing fabrics using the knitting procedure. c) Crocheting: In order to make sweaters, made of wool and cotton. d) Weaving: A length-wise subjective yarn to use for a greater purpose. e) Embroidery: Yarn is applicable for embroidery as well. f) Ropemaking: Using textile yarn, rope-making seems easier than before. #FAQs: 1. How Can I Differentiate between Fiber and Yarn? Answer: Fibers can be both natural and man-made or synthetic. For example, natural fiber: Cotton, wool. Man-Made or Synthetic Fiber: Acrylic and Polyester. Yarns are made from these two ranges of fibers. 2. What are the different properties of Yarn? Yarn usually has the following properties. Such as: Plasticity Elongation Strength Twist variation Elasticity.