Lack of getting enough information about what is a Staple yarn? Are you confused about whether the staple yarn has any manufacturing process or any sources of materials? This article will inform you about staple yarn and how it differs from other yarns.
Table Of Contents
What is a Staple Yarn?
A yarn that forms from short-length staple fibers (wool, flax, cotton, jute) is known as staple yarn. The staple yarn has another name that is “Spun yarn.”

Here, staple yarns get twisted to form the “spun yarn.” The staple yarn comes from wool, cotton, flax, or any other natural sources except for Silk. Even, Staple yarn comes from man-made fibers, instances-viscose, polyester, nylon, and acrylic, which are filament constructed.

To create staple yarn, they get cut down into small lengths with spun together. The short length makes them look like natural fibers. The length of staple fiber is less than 7”. The staple yarn length determines the material quality. That means High quality depends on the long staple.
What is Staple Yarn made of?
The staple yarn has 3 sources, named as Natural, Synthetic, and Blend. Among these three sources, the staple yarn comes from natural (cotton, rayon, linen, wool, flax, jute, etc). After that, polyester, nylon, and acrylic are there as synthetic sources to form staple yarn. There is a polyester cotton blend that makes another source of staple yarn. Other than these 3, there are two forms of staple yarn.
That is parallel fiber yarns and condenser spun or non-parallel fibers. Parallel fibers can be both long and short staple fiber yarns. They tend to be straight like the parallel to any product axis before getting twisted. Here, fibers are not parallel yet randomly arranged before spinning. Staple yarns get attached by a twist. Here, the twist can be either an S or Z twist. In the S twist, the threads go up and turn left. In a Z twist, the threads go up and turn the right.
Staple Yarn Formation: Staple Yarn Spinning Process
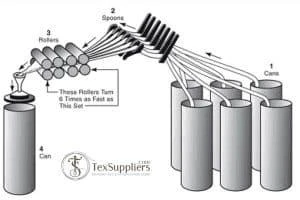
The formation of staple yarn involves several steps that include:
Step 01: Fiber Cleaning and Opening
In this process, natural fiber cleaning and opening are used.
Step 02: Fiber Blending
This step is to assure uniform mixing in fiber blends
Step 03: Carding
This step is to align fibers also to remove the short fibers.
Step 4: Combing
This step requires desired and aligned fibers.
Step 5: Drawing and Spinning
It is to reduce the yarn denier and to provide a suitable twist and cohesion.
Step 6: Yarn Twisting
Twisting requires providing yarn a great uniformity.
As per the steps, it is indeed inevitable that the staple yarn has a complex manufacturing process.
Manufacturing Process in Brief
The Cotton system is the widely used source of staple fibers. At first, fibers run through the spiked rollers to pull apart the clumps. After that, they get separated in the cleaning step with trash being removed. Then, fibers pass through the wires to get separated and aligned. They emerge as silver yet aligned fibers. To remove the short-length fibers, silver can get combed. In the finishing, these cotton fabrics turn into fine-combed cotton.
The wool fibers can get prepared for spinning in the same way. Carded fibers convert into woolen yarns. The worsted yarns get subjected to a gilling process. It helps to straighten up the fibers.
Techniques for Twisting Staple Yarns
Among the several techniques to get the staple yarns inserted in the final twist, ring spinning, and open-end spinning are the most common processes.
Rotor Spinning:
An existing yarn catches the fibers. The rotor twists and rotates the yarn. Rotor Spun yarns are uniform yet weak yarns. Most denim-made cotton yarns are rotor-spun.
Friction Spinning:
This is another open-end method. Between two drums, rotating in opposite directions, a mixture becomes fed. This process allows twists to get into the fibers.
Air-Jet Spinning:
Air-forcing jets of the outer layers form yarns using this air-jet spinning method. But these yarns are weaker but possess fine sizes.
Types of Staple Yarn
Asian Cotton
There are no specific types of staple yarn. But cotton staple fibers have 4 major groups to identify. These are:
Pima Cotton

This is the second-longest staple cotton. We may find this cotton in Peru, Egypt and the Southwest U.S.
Sea Island Cotton

The best quality cotton in the world is Sea Island cotton. The finest length of this cotton is 2-(1/4)”. This type of cotton is available in Georgia, Florida, and South Carolina. These kinds of cotton are available in Asia, Japan, China, and Pakistan. The length is not more than 2 inches.
The U.S. Cotton

These are the cotton of the United States no longer than 1.5 inches.
Properties
|
Durability |
Moderate |
|
Appearance |
Flat, Dull, Fuzzy |
|
Breathability |
Better |
|
Strength |
Reasonable |
|
Sustainability |
Moderate |
|
Comfortability |
High |
|
Water Resistant Abilities |
Yes |
|
Wrinkle-Resistance Abilities |
Yes, Polyester Staple Fiber |
|
Comfort Rating |
Good |
|
Uniformity |
Reasonable |
|
Fabric Handling |
Excellent |
|
Covering Power |
Good |
|
Applications |
Knitting, Crocheting, Clothing, Carpet Manufacturing, upholstery |
Characteristics of Staple yarns
- Yarn Count: A Weight (/unit) Length System
- Less Shiny in Appearance.
- Rough to touch.
- Does not slip away.
- Short-length fiber (from 35 ~ 150 nm)
- Absorbent in Nature
- Has a Complex Manufacturing Process
- Requires Multiple twists
- Elastic Recovery is Poor
- Less Snagging
Applications of Staple yarns
In the case of Staple yarn, twisting is important. We need to twist the staple yarn very tightly to keep the fibers together. The Staple yarn has a wider diameter. The application area of this staple yarn is the production of clothing, the manufacture of carpets, crocheting, and knitting. The staple yarn-made clothes are hairy in appearance. They are the most useful in making clothes for winter.
Conclusion
Staple yarns are easily recognizable as short-length fibers. It has multiple forms, twist types, and a complex manufacturing process. Although staple yarn has broad three sources, they get weak when compared to other yarns’ strengths. They are not lustrous at all and tend to pill better comparatively.















Comments - 00
Leave A Reply
Thanks for choosing to leave a comment.