Filament yarn has a robust manufacturing process. The fibers are mostly synthetic in nature. Due to the rise in the demand for polyester and viscose filament yarns, the manufacturing process becomes an indispensable factor. In this article, we will be reviewing the manufacturing process of viscose filament and polyester filament yarns.
Table Of Contents
What is Filament Yarn?
A filament yarn refers to the continuous strands that run the whole yarn length with component filament. The yarn composing only one filament is known as monofilament yarn. Meanwhile, yarns that contain more than one filament are well-known as multi-filament yarns.

The main component of filament yarn is nothing but synthetic fibers. Among those components or elements, silk is the major one. Filament yarn is also classified as both flat and bulk. Flat filaments are closely packed with smooth surfaces and bulked yarns are crimped and entangled.
Manufacturing Process of the Filament Yarn: Polyester
The finished polyester will have the basic forms including filament, staple, tow, and fiberfill. Here, in the filament yarn, the polyester fiber strand is continuous in case of length and produces a smooth surface.
-
Polymerization
In order to form polyester, we need dimethyl terephthalate to react with the ethylene glycol in the catalyst presence at a temperature of 302-410 degrees Fahrenheit. Here, the chemical, monomer alcohol gets combined with the acid named terephthalic. The acid then gets raised to a temperature of 472 degrees Fahrenheit.
-
Drying
After the polymerization process, the molten ribbons get cool until they turn brittle. The material is then cut into small chips and dried to prevent any odd irregularity.
-
Melt Spinning
Polymer chips tend to be melted at the temperature of 500-518 degrees Fahrenheit to form a solution similar to syrup. The solution then gets put in a metal container named a spinneret. The spinneret holes determine the yarn sizes because the fibers form a single strand. At the spinning stage, chemicals get added to the solution while making the material flame retardant.
-
Fiber Drawing
When polyester emerges, it becomes soft and easy to elongate according to the original length. The stretching forces the polyester to be aligned.
It increases strength and tenacity. Filaments become dry as the fibers become strong. Besides, the drawn fibers vary in both diameter and length. It depends on the desired finished material. During the fibers drawing, they get textured and twisted. It creates a softer fabric pattern.
-
Winding
After drawing the polyester yarn, it gets wound on the flat-wound package in order to be woven in the material-like thing.
Manufacturing Process of the Filament Yarn: Viscose
Viscose filament yarn creates fabric both for clothing and home furnishings. It appears as silky and feels smooth. Its ability to breathe and absorb liquid is highly satisfactory.
Production Process of the Viscose Filament Yarn
The cellulose reaction has been used with caustic soda in making the viscose filament yarn. During the ripening process, a depolymerization theme occurs. Here, carbon disulfide gets added. It produces cellulose xanthate. It is an orange-colored crumb that dissolves in caustic soda. It produces an orange-colored solution.
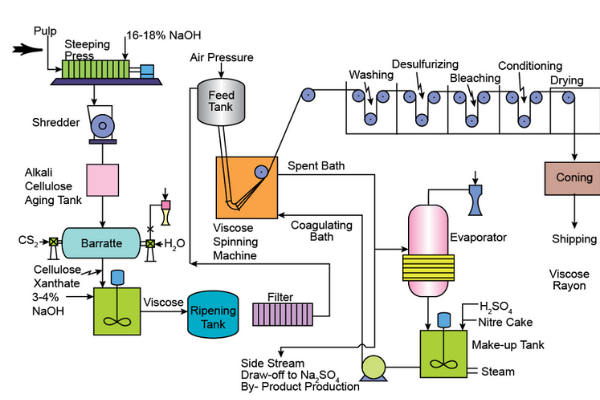
While the xanthate is decomposing, the solution gets pumped through a spinneret. Here, cellulose is well-regenerated as the “fine” filaments. After that, the purified cellulose gets mercerized with NaOH and xanthate. They dissolved in NaOH intending to form a solution of spinning named spun.
Step-by-step Process of Viscose-Manufacturing
Viscose filament yarn has huge demand in the international market. The increase in the price is also an indication of the extensive manufacturing process. The process is described here step-by-step:
-
Wood Pulp Preparation
Wood chips get treated with calcium bic-sulfide. After that, they get cooked under steam pressure.
-
Steeping
To swell the cellulose fibers and transform the cellulose, the pulp gets immersed in 17-20% aqueous NaOH (Sodium hydroxide) at 18 to 25 degrees Celsius.
-
Shredding
Pressed alkali cellulose gets shredded down. Here, the move increases the surface area of the cellulose. It improves the ability to react as follows.
-
Aging
Here, the depolymerization of the cellulose to the polymerization desired degree. The alkali cellulose gets aged under a regulated time. Here, the temperature conditions are between 19 to 30 degrees Celsius.
-
Xanthation
Here, the step involves placing the aged alkali cellulose. It allows them to react with carbon desulphated at a temperature. Here, it is to produce cellulose xanthate.
-
Dissolving
The cellulose xanthate gets dissolved in an aqueous caustic solution form. The cellulose viscosity gets extremely high.
-
Ripening
For a period, the viscose can get ripen. At the time of ripening, two essential processes occur in two classes: redistribution and xanthate loss.
-
Filtration
Here, the viscose gets filtered to eliminate any undissolved material. It interferes with the spinning.
-
Degassing
Air-trapped bubbles in the viscose must be removed before extrusion. The fine rayon filament develops voids.
-
Wet Spinning
The viscose solution gets metered. It gets metered into a spin bath. It contains sulphuric acid, sodium sulfate, and zinc sulfate via spinneret with holes.
-
Drawing
The rayon filaments get extended although the cellulose chains are mobile.
Conclusion
The fibers used in the manufacturing process are synthetic textile fibers. Here, they get obtained by esterification of the dicarboxylic acids. In both cases, there are uses of acids-both organic and mineral. In the case of viscose, there are wood pulp or cotton linter that get used to making it. Because of its brightness, viscose was the first artificial silk. Both polyester and viscose yarn has the benefit of being available throughout the world and having a significant role in the garment industry.





















Comments - 00
Leave A Reply
Thanks for choosing to leave a comment.